Abstract
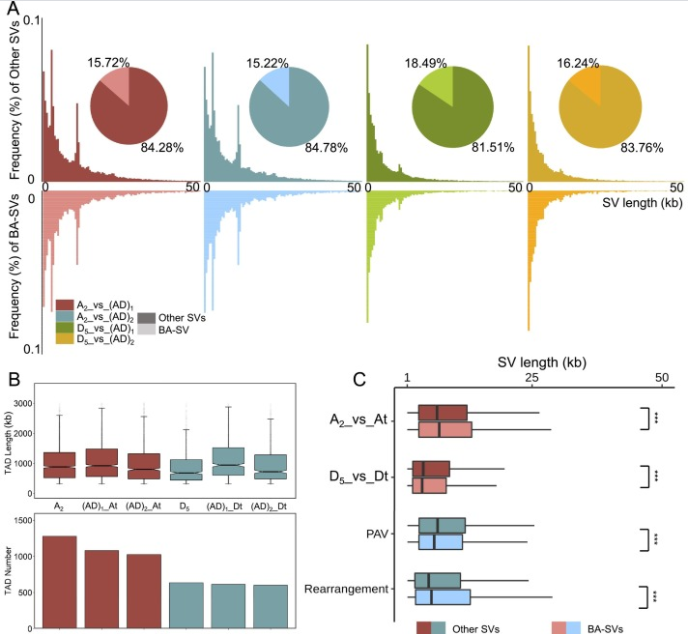
Structural variations (SVs) are recognized to have an important role in transcriptional regulation, especially in the light of resolved 3D genome structure using high-throughput chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C) technology in mammals. However, the effect of SVs on 3D genome organization in plants remains rarely understood. In this study, we identified 295,496 SVs and 5251 topologically associating domains (TADs) in two diploid and two tetraploid cottons. We observed that approximately 16% of SVs occurred in TAD boundary regions that were called boundary affecting-structural variations (BA-SVs), and had a large effect on disrupting TAD organization. Nevertheless, SVs preferred occurring in TAD interior instead of TAD boundary, probably associated with the relaxed evolutionary selection pressure. We noticed the biased evolution of the At and Dt subgenomes of tetraploid cottons, in terms of SV-mediated disruption of 3D genome structure relative to diploids. In addition, we provide evidence showing that both SVs and TAD disruption could lead to expression difference of orthologous genes. This study advances our understanding of the effect of SVs on 3D genome organization and gene expression regulation in plants.
原文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0888754321003013?dgcid=author