Summary
Global warming has reduced the productivity of many fieldgrown crops due to effects on male sterility.
The genetic regulation of high temperature (HT) response in the major crop cotton is poorly understood.
We determined the functionality and transcriptomes of anther of 218 cotton accessions grown
under HT stress. By analyzing transcriptome divergence and implementing genomewide
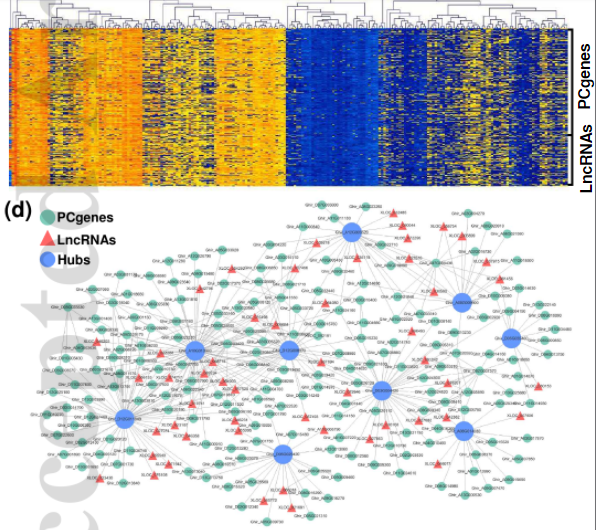
association study (GWAS), we identified three thermal tolerance associated loci which contained 75
protein coding genes and 27 long noncoding RNAs, and provided expression quantitative trait loci
(eQTLs) for 13,132 transcripts.
A transcriptomewide association study (TWAS) confirmed six causal elements for the HT response
(three genes overlapped with GWAS results), involved in protein kinase activity. The most
susceptible gene, GhHRK1 was confirmed as a previously uncharacterized negative regulator
of the HT response both in cotton and in Arabidopsis.
These functional variants provided new understanding of genetic basis for HT tolerance in male
reproduction organs.
-
原文链接:https://nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/nph.17325