Abstract
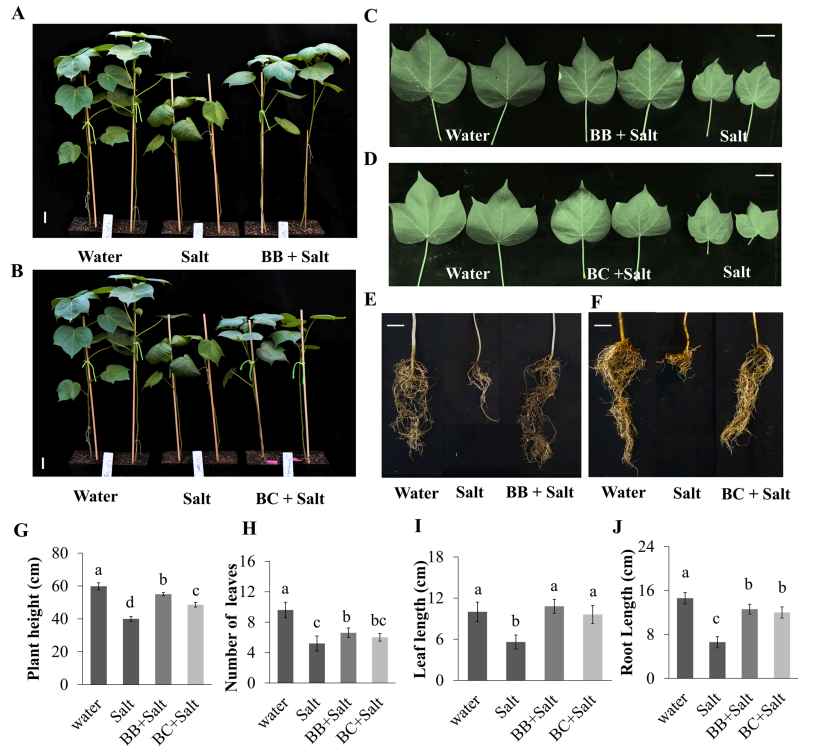
Soil salinity is a major constraint for reducing crop productivity worldwide. To combat this situation, the current project was aimed to examine the effect of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) inoculation on the growth of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum, var. Jin668) plants during salt stress and to identify salt stress-responsive genes in cotton plants. For this purpose, two bacteria, Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus pumilus were selected among the 20 strains isolated from the cotton rhizosphere under the salt stress (200 mM NaCl) and identified by 16 S rRNA sequencing. B. subtilis and B. pumilus were applied to Jin668 plants under salt stress which enhanced resistance to salt stress (leaf and root growth) compared to only salt-treated plants and control plants. Transcriptomic analysis revealed 556 differentially expressed genes (481 up-regulated and 75 down-regulated) in the B. subtilis + Salt versus Salt treatments and 943 (536 up-regulated and 407 down-regulated) genes in the B. pumilus + Salt versus Salt treatments. KEGG analysis of B. pumilus + Salt versus Salt and B. pumilus + Salt versus Salt revealed the pathways plant-pathogen interaction and plant hormone signal transduction were expressed in both treatments, while ascorbate and aldarate metabolism pathways and glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism pathways were uniquely expressed in the B. pumilus + Salt versus Salt comparison, and the pentose and glucuronate interconversions pathway was uniquely expressed in the B. pumilus + Salt treatment versus Salt comparison. These data showed that B. subtilis and B. pumilussignificantly enhance salt stress tolerance in cotton plants during salt stress conditions.
full text https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098847222001502